IDEA插件开发(七)mybatis插件之mapper解析 一文中使用到了PropertyConverter来为property属性添加引用,实现鼠标点击跳转,代码补全提示等功能,其中使用了ContextPsiFieldReference,它继承了PsiReferenceBase,实现resolve()方法来返回对应的引用对象。
今天主要就说说引用( PSI References ),以及如何单独注册引用。
A reference in a PSI tree is an object that represents a link from a usage of a certain element in the code to the corresponding declaration. Resolving a reference means locating the declaration to which a specific usage refers.
Resolving references gives users the ability to navigate from a PSI element usage (accessing a variable, calling a method and so on) to the declaration of that element (the variable’s definition, a method declaration and so on). This feature is needed in order to support the
Go to Declarationaction invoked by Ctrl-B and Ctrl-Click, and it is a prerequisite for implementing the Find Usages action, the Rename refactoring and code completion.
举个例子,也就是我想要实现的效果。
Dao层有个方法:
然后对应的mapper文件中的查询语句:
我现在想实现点击#{userName}中的userName能够跳转到Dao层方法的userName参数,即为xml中的参数添加引用。
要实现这样的功能,有两个关键点:
- 创建一个
PsiReferenceBase引用类,实现resolve()方法,返回值为当前PsiElement需要跳转到的目标PsiElement。 - 继承
PsiReferenceContributor,实现registerReferenceProviders()方法,将创建的引用类注册(绑定)到一个触发PsiElement上。可以理解为点击哪个元素会触发引用跳转。
引用绑定注册器PsiReferenceContributor
按照逻辑,我们需要先找到触发元素,本例中,就是先要从mapper文件中找出#{userName}中的userName,即符合#{paramName}模式的参数名。然后将引用绑定到该元素上。
寻找和绑定的逻辑需要放到PsiReferenceContributor中:
重点在于registerReferenceProvider的两个参数。
第一个参数传入PlatformPatterns.psiElement(XmlToken.class),代表我们要为XmlToken添加引用。
为什么说我们要为XmlToken添加引用呢?因为mapper的xml文件中,最基本的元素就是一个XmlToken,user_name是一个,like是一个,CONCAT('%',#{userName},'%')是一个。
可以简单的理解为,使用空格分割的元素都是。
为了分析IDEA中的元素从属于哪种PsiElement类型,可以给沙箱安装一个插件PsiViewer,然后就可以方便的分析PsiElement类型了:
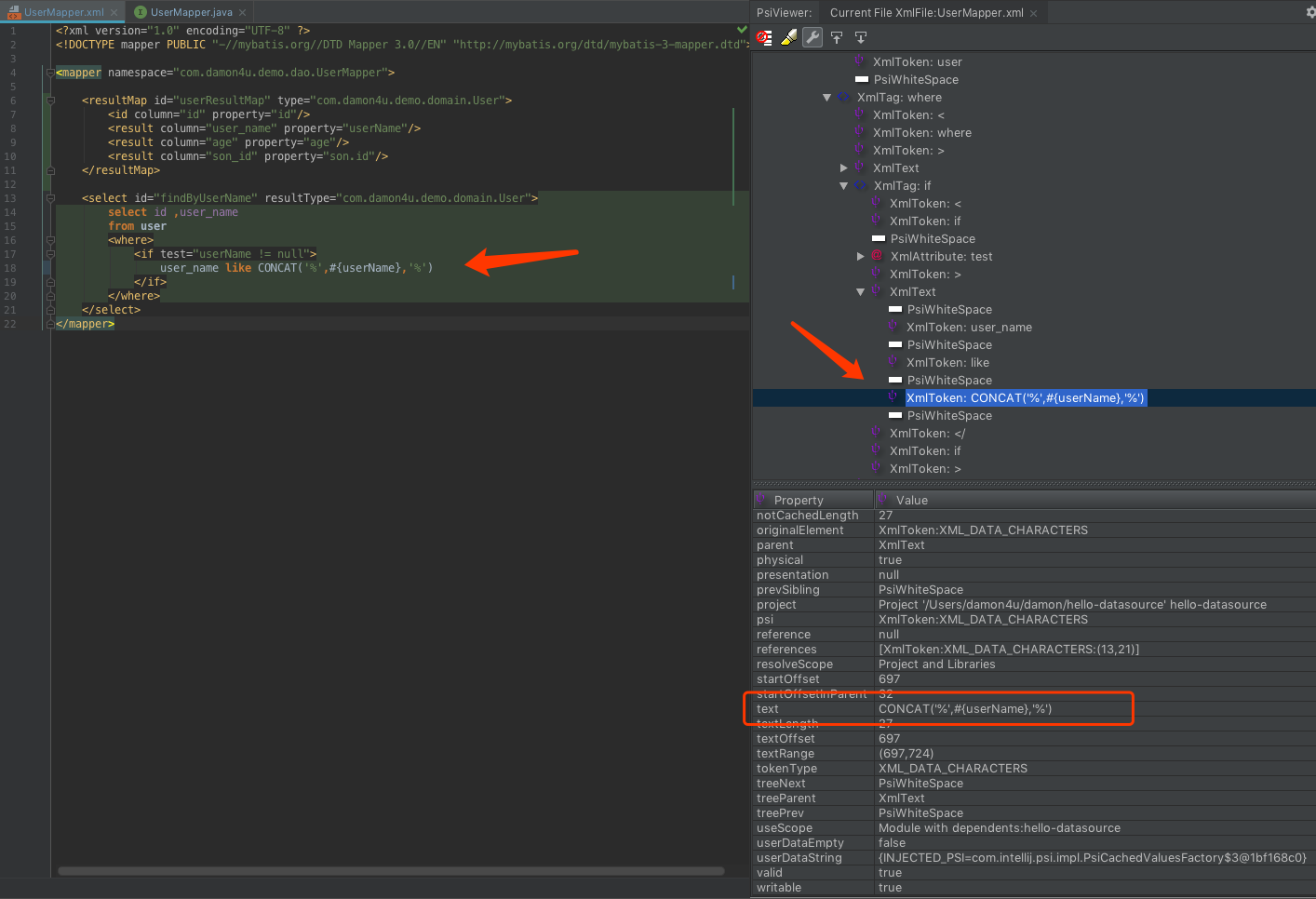
鼠标点击要分析的元素上,右边能清晰的看到元素的属性以及层级关系。
第二个参数是PsiReferenceProvider实现类,主要实现getReferencesByElement方法,将引用绑定到指定元素上。
由于所有xml中的XmlToken都会被放到候选集中,我们需要过滤出想要的元素,必须在mapper文件内。
DomUtils.isMybatisFile(psiFile);方法比较简单,就是比较根标签是否是mapper。
之后,使用正则表达式取出符合#{paramName}模式的参数名,以及参数名在XmlToken中的开始位置和结束位置,构造一个TextRange,作为鼠标点击区域。
之后构造一个我们自己的引用实例ParamReference,加入到返回列表中,完成绑定。
引用PsiReferenceBase
接下来就要下我们自己的PsiReferenceBase了:
其中设计到JavaUtils中的几个方法,寻找mapper对应的dao层方法:
最后,将SqlParamReferenceContributor注册到plugin.xml中:
至此,便完成了对sql语句中#{userName}的引用创建。
下面再举一个例子,并说说开发时遇到的坑。
回到刚才的mapper文件中的查询语句:
我现在还想为<if test="userName != null">中的userName添加引用,同样跳转到Dao层方法参数。
思路一,完全复用SqlParamReferenceContributor
使用PsiViewer分析<if test="userName != null">也属于XmlToken类型,那理论上SqlParamReferenceContributor也能接收到。
但是反复Debug都没有拦截到这个值。后来发现,只有XmlText下的XmlToken才能被拦截到。
那可能是PlatformPatterns.psiElement(XmlToken.class)这种创建Patterns的方式有问题,只能拦截XmlText下的XmlToken,不能拦截XmlAttributeValue下的XmlToken。
所以这个思路不行。
思路二,匹配XmlAttribute
只要能取出所有mapper中的XmlAttribute,然后比较name是否为test,如果是,取出XmlAttributeValue,匹配关键字创建引用即可。
开发过程中,发现匹配没问题,但是会把引用绑定到XmlAttribute整体上,test="userName != null"。
其实我们真正想要的是给XmlAttributeValue创建引用,即"userName != null"部分。
思路三,匹配XmlAttributeValue
最开始也是想匹配XmlAttributeValue的,但是不好过滤前面的test。所以想简单的匹配XmlAttribute,然后比较name是否为test。XmlAttributeValue其实是XmlAttribute的子标签,获取父类即可拿到XmlAttribute。
下面看实现:
其中引用可以复用之前的ParamReference。
最后不要忘了注册到plugin.xml中:
参考:
PSI References
References and Resolve
Reference Contributor